
CATCH-Seq Technology
The proprietary CATCH-Seq targeted sequencing technology leverages genomic clones to generate probes corresponding to large, contiguous blocks of a genome such as MHC loci. This is particularly useful when your research calls for sequencing coding and non-coding regions of a gene, including introns and flanking sequences. Sequencing large target regions including introns make it ideal for identification of structural variants and CNV’s.
CATCH-Seq target enrichment is also ideal for studies of DNA methylation, by performing targeted bisulfite sequencing after the target enrichment steps. CATCH-Seq target enrichment technology is compatible with any NGS library or platform. Best of all, since CATCH-Seq technology requires no oligonucleotide design and production costs, custom capture reagents are available at a fraction of the cost of other target enrichment methods.
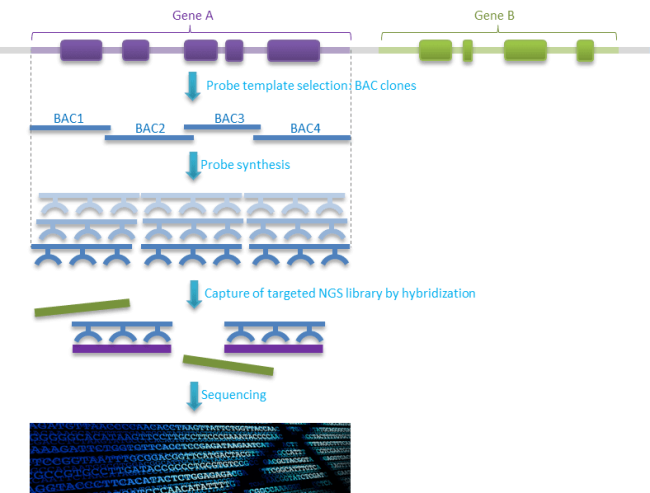
Advantages of CATCH-Seq
- Large target regions: CATCH-Seq capture probes can cover several hundred kilobases to several megabases of contiguous sequence and can cover exons, introns, 5’ regulatory regions, 3’ regulatory regions, and flanking regions.
- Greater specificity with longer probes (200-300bp)
- Better coverage of the targeted region including repeats
- Significantly lower cost than oligo-based probes
- Multiplexed capture of samples reduces costs
Publications using CATCH-Seq
- Targeted sequencing of large genomic regions with CATCH-Seq.
PLoS One. 2014 Oct 30; 9(10):e111756. PMID: 25357200 - Epigenome-wide association study of fasting blood lipids in the Genetics of Lipid-lowering Drugs and Diet Network study.
Circulation. 2014 Aug 12; 130(7):565-72. PMID: 24920721 - Regulation of DNA methylation dictates CD4 expression during the development of helper and cytotoxic T cell lineages.
Nat Immunol. 2015 Jul; 16(7):746-54. PMID: 26030024 - Recurrent evolution of melanism in South American felids.
PLoS Genet. 2015 Feb 19;11(2):e1004892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004892. PMID: 25695801 - A deletion at ADAMTS9-MAGI1 locus is associated with psoriatic arthritis risk.
Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Oct;74(10):1875-81. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-207190. PMID: 25990289 - dCATCH-Seq: improved sequencing of large continuous genomic targets with double-hybridization.
BMC Genomics 2017:18, 811. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4159-7 - Stage-specific epigenetic regulation of CD4 expression by coordinated enhancer elements during T cell development.
Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 5;9(1):3594. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05834-w. PMID: 30185805 - Whole Blood Targeted Bisulfite Sequencing Validates Differential Methylation in C6ORF10 gene of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.
J Rheumatology. 2019 Nov; jrheum.190376; DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.190376 - TET proteins regulate T cell and iNKT cell lineage specification in a TET2 catalytic dependent manner.
Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 5;13:940995. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.940995. PMID: 35990681; PMCID: PMC9389146. - CD4 expression in effector T cells depends on DNA demethylation over a developmentally established stimulus-responsive element.
Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 18;13(1):1477. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28914-4. PMID: 35304452
